IEEE standard 802.11r explains about roaming concepts ,
Roaming always helps to get rid of initial connection process and allows clients to stay connected when station or client is move from one pace to other i.e station or client does initial handshake to targeted AP before it client roams. This mechanism can help client to roam seamlessly from AP1 to AP2 without losing connectivity (less then 5 ping loss are expected)
In 802.11r roaming we support two methods
Fast BSS Transition Over the Air
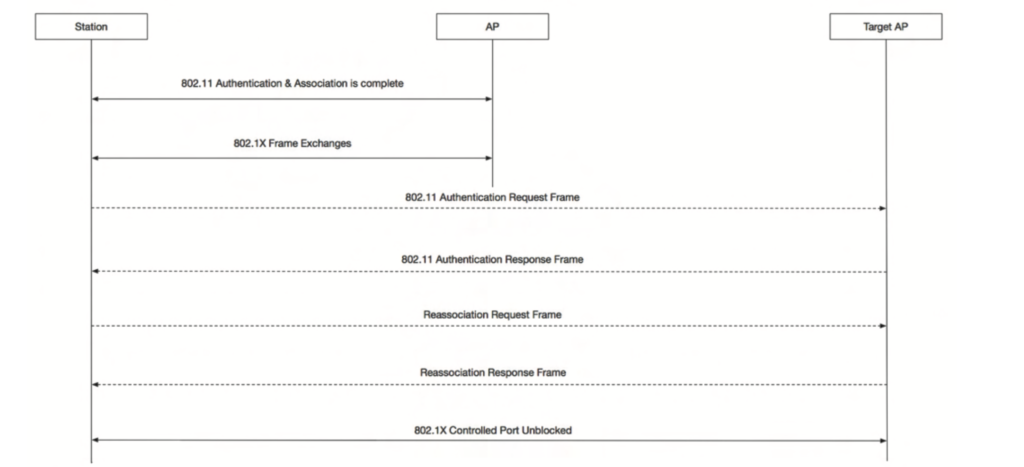
Over-the-Air mechanism helps station and AP to derive PTK by exchanging below messages
Frame 1: Client transmits FBT Auth Request(Which is also termed as FBT Auth1) frame to Target AP
Frame 2: Target AP transmits FBT Auth Response (Which is also termed as FBT Auth2) frame to the Client
Frame 3: After receiving the FBT Auth Response,Client transmit Re-Assoc Req to target AP
Frame 4: After receiving the Re-assoc Req, AP will transmits Re-Assoc Response with the status code as success.
Note:
In Fast BSS Transition roaming over-the-Air, the Mobility domain element will be present in Beacon, Probe response, Auth ,and reassoc frame. If the Mobility domain IE received by the AP from Clients are not matching with beacon,probe response then AP will reject Auth req
If the PMKID present in the FBT-Auth request not match with PMKID present on AP then AP will reject the FBT Auth Req frame
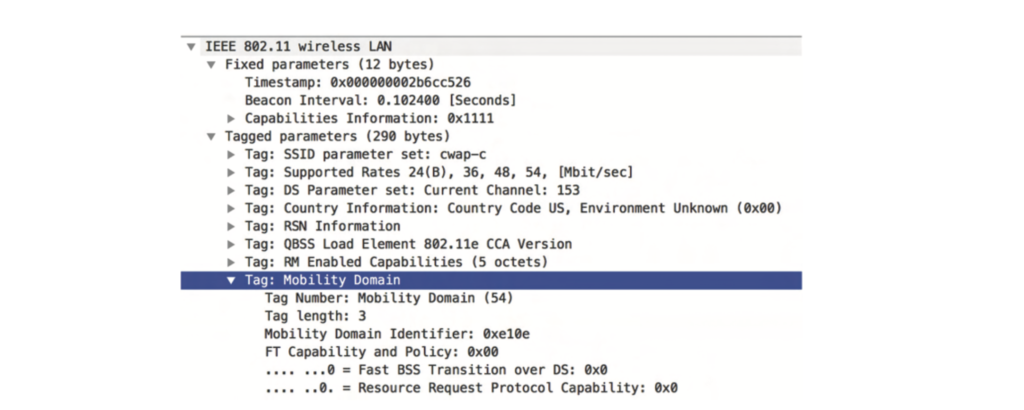
Mobility domain IE is used to validate the FT (Fast BSS Transition) mechanism is Over-the-Air or Over-the-DS, in above snippet Mobility IE demonstrates that FT over DS is set to 0 means that Fast BSS Transition under use is Over-the-Air.
Fast BSS Transition Over-the-DS
The FT Transition over-the- DS(Distributed system ) is used when a client roams to target AP over the distributed system.
In case of Over-the-DS initial handshake always take place with help of current AP. Below handshake can help to identify how does OVer-the-DS handshake takes place
Frame 1: Client transmits FT request frame to current AP with the target AP address field set to the target AP BSSID
Frame 2:The target AP sends FT response frame to client
Frame 3: After receiving FT response, client sends Re-Assoc Request frame directly to target AP
Frame4:After receiving Re-Assoc request ,target AP validate and send Re-Assoc Response to Client

Note:
As Fast BSS transition over-the-air is widely used in enterprise industry .
In Enterprise domain we have observed most the vendor based on requirement uses anyone of roaming mechanism i.e 11r roaming,PMKC roaming,OKC roaming
11r Roaming:
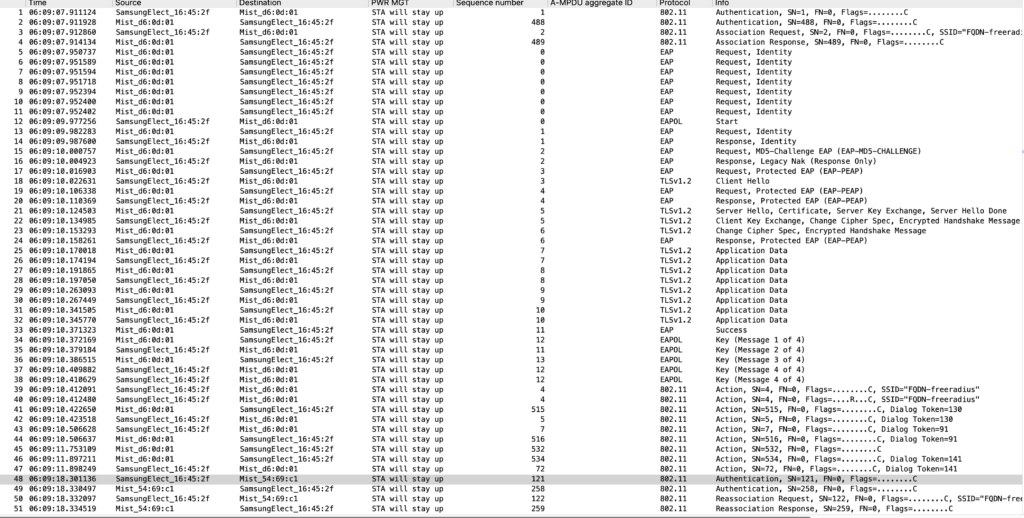
Intially client does full auth with AP1 (current AP) i.e client does PEAP enterprise security handshake with the AP1 and later the PMKID is distributed above other neighbor AP (such AP2,AP3 etc..) t, once client decide to roam from AP1 to AP2 (target AP) then client does sends FBT auth to AP2 and followed by FBT Auth response from AP2 . Later clients sends Re-Assoc Req to AP2 and AP2 sends Re-assoc response with status code as success.
PMKC Roaming :
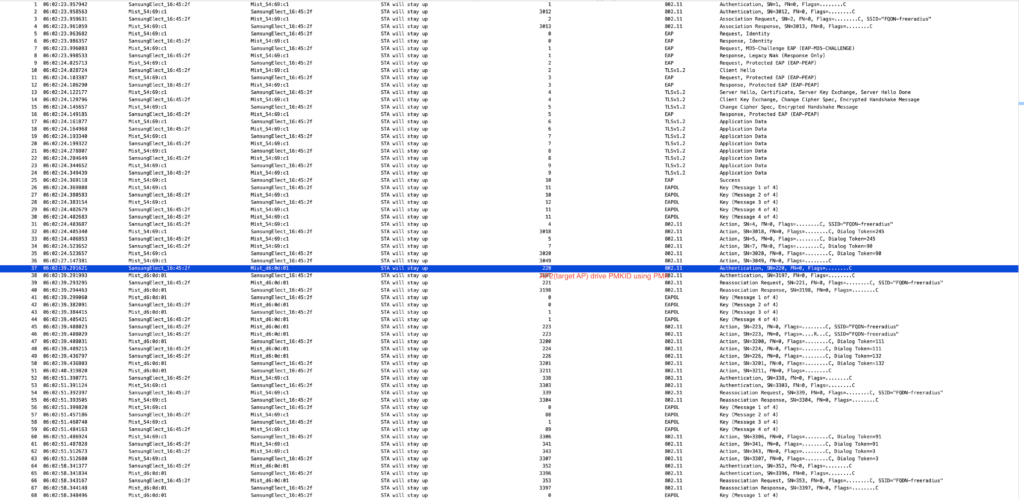
In PMKC roaming when client roams from AP1 to AP2 ,AP2 don’t have PMK info hence client always does full auth with AP2 for very first time and later if client roam back to AP1 then it does auth and reassoc and followed by EAPOL 4-way handshake to derive PTK and GTK

OKC Roaming :
Intially client does full auth with AP1 (current AP) i.e client does PEAP enterprise security handshake with the AP1 and later the PMK is distributed above other neighbor AP (such AP2,AP3 etc..) t, once client decide to roam from AP1 to AP2 (target AP) then client does sends FBT auth to AP2 and followed by FBT Auth response from AP2 . Later clients sends Re-Assoc Req to AP2 and AP2 sends Re-Assoc response with status code as success and followed by 4-way EAPOL handshake
References :
Certified Wireless Analysis Professional -Chapter5
Note: All diagram are taken from references