Below Mac layer enhancement proposed for 802.11n Protocol
Frame Aggregation
Frame aggregation is a method of combining multiple frames into a single frame for tx which can help to reduce MAC layer overhead.
Note:
Overhead is something to avoid random backoff for every single frame transfer over channel.
A-MSDU:
When Multiple MSDU (Mac service data unit) combined into single MSDU then its called as A-MSDU (aggregated Mac service data unit)
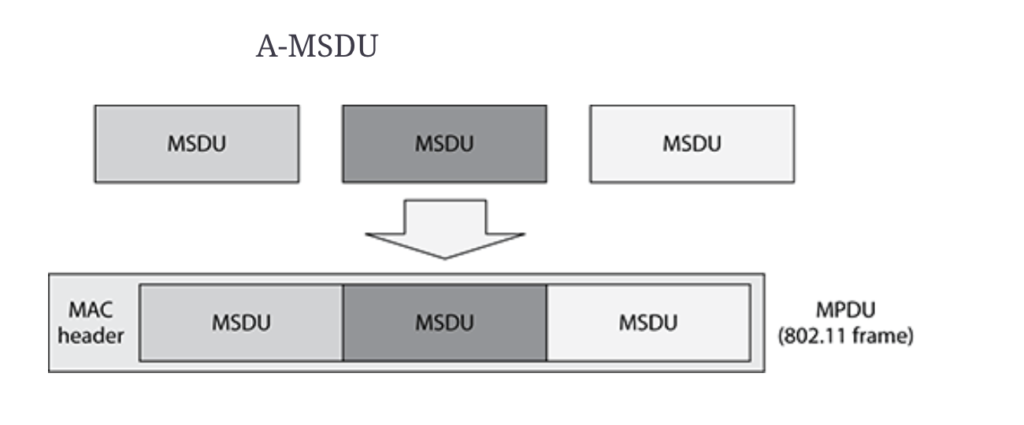
The aggregated MSDUs will have a single destination when wrapped together in a single frame.The SIZE of A-MSDU does not exceed the maximum A-MSDU size capable of receiving station. A-MSDU should have all MSDUs with the same QoS access category.
Note: length information is present in HT capabilities field and STA maximum length can be 0 = 3839 bytes or 1 = 7935 bytes
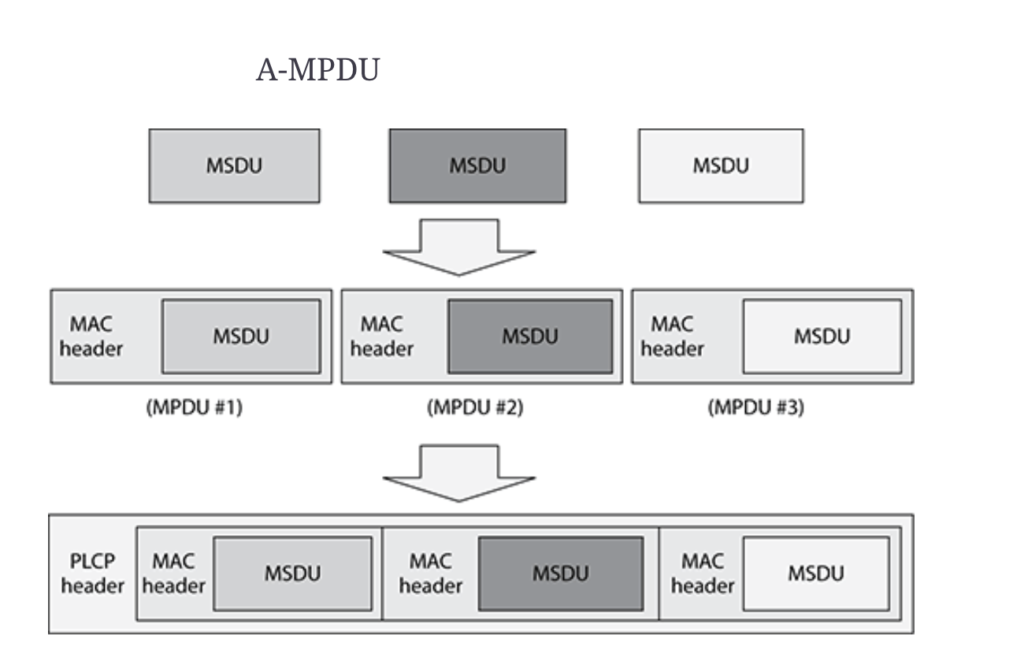
A-MPDU:
When multiple MPDUs aggregated into a single MPDU then it called as Aggregated MPDU( A-MPDU)
The receiving address of Individual MPDUs within an A-MPDU must be same also the individual MPDU should have same QoS access category.
Maximum size of an MPDU with in A-MPDU is 4095 bytes.
Below is A-MPDU Parameters field of the HT Capabilities Element contains Maximum A-MPDU Length Exponent.
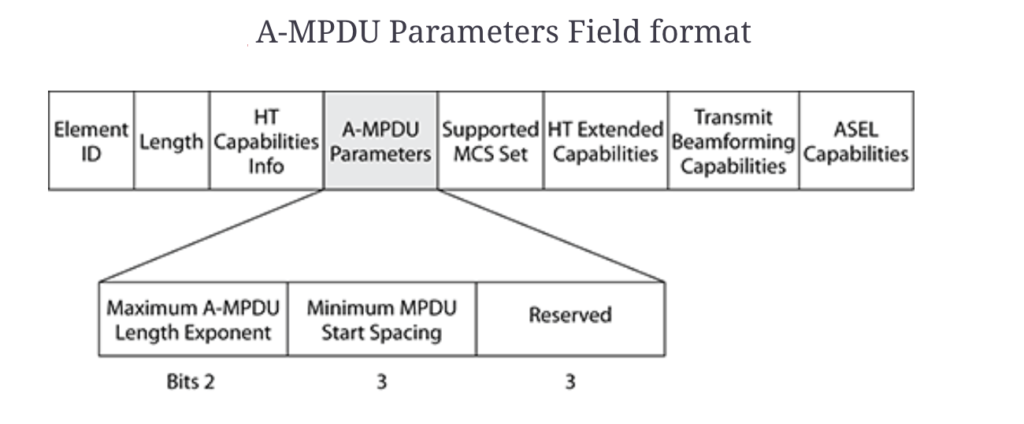
A-MPDU Length Exponent subfield might be 0 as 8K or 1 as 16K or 2 as 36K or 3 as 64K.
Below A-MPDU Parameters to be verified for size

HT-Delayed BlockAck
BlockAcks was introduced in 802.11e to improve the efficiency of MAC operations. In 802.11n Block Ack mechanism is made mandatory ,so 802.11n got introduced with new enhancement of Block ack that is called as delayed block ack
In below figure mechanism of delayed block is explained ,in short Delayed block is sent from AP when all transmission of data is over.

802.11n Power Management:
Powersave mechanism introduced in 802.11n are power save multi-poll (PSMP) and spatial multiplexing power save (SMPS).
PSMP(Power Save Multi Poll):
PSMP is a power management based on scheduled automatic power save delivery (S-APSD).Its based out of hybrid coordination function controlled channel access, where AP assigning service periods for stations to transmit and receive frames.
Unscheduled PSMP is used in 802.11n and it is same as that of U-APSD
SMPS(spatial multiplexing power save):
SMPS is similar to PSMP. SMPS allows a client to turn off some of its spatial streams during periods of inactivity as part of power save Once client overcome powersave period or got to infromed by AP (at DTIM interval) then client needs to wake up and receive data and it can activate the necessary spatial streams.
Reference:
802.11 Standard
CWAP-chapter 10
Note: All diagram are taken from references