Open Authentication to the Access Point
In open auth, station or client sends an authentication request (Auth1) to the AP, which the AP accepts sends authentication response (Auth2) frame. then station sends association request to AP and AP sends association response ,after successful assoc response , station or client supplicant connects to AP using open auth to transfer data client need to have ip so client does DORA process to get IP.

Sniffer capture analysis for open security:
In below example : Initially client does passive scanning and active scanning both, in active scanning client will send out probe req frame with broadcast mac address as destination mac and Access point responds with Probe response unicast to client . then client initiate auth 1 frame ,AP response with auth 2 and later client sends assoc request frame and AP responds to the same .
Beacon of open auth:

Probe request from client:

Probe response from AP:

Auth1 from client:

Auth2 from AP:

Assoc Req from client:
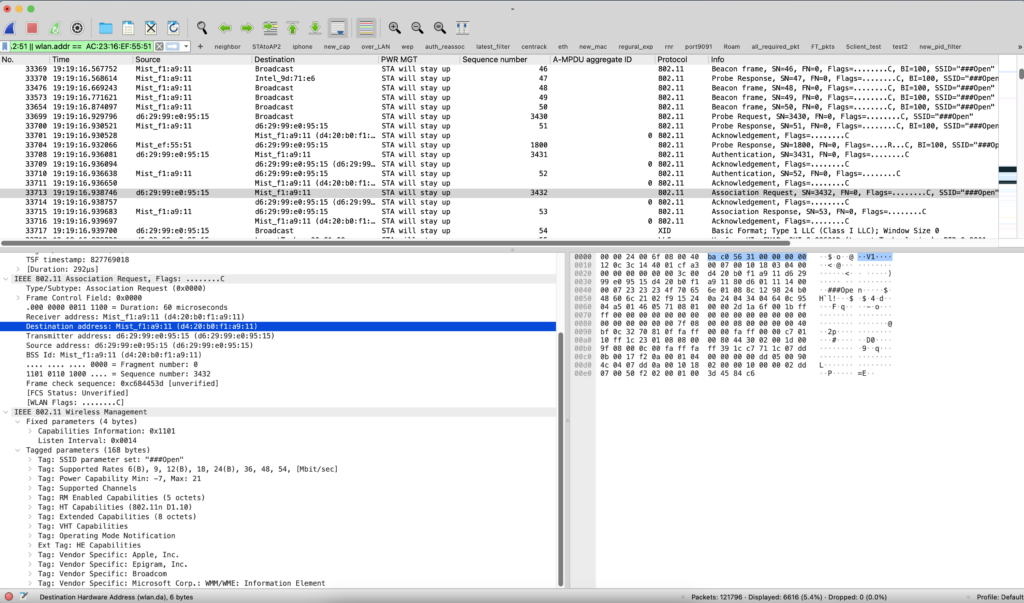
Assoc Resp from AP:

Overview of open security handshake between client and AP:

There are few cases where client need to roam between AP1 to AP2 using open security . In open security we have 4 frame exchange so there is no overhead hence client and AP2 need to follow open security handshake (auth1,auth2 ,Reassoc req and Reassoc resp )

Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
WEP supports two auth methods:
- Open authentication
- Shared key authentication
Open WEP authentication is same that of open authentication, as mentioned above.
Shared key authentication uses RC4 cipher algorithm to encrypt frame . The process is client sends a request for auth request to AP to start shared key authentication . AP sends the response by generating the challenge text and client encrypt the challenge text using the key entered by user then sends encrypted challenge text to AP ,then AP after receiving the encrypted challenge text try to decrypt the challenge text using same key and compare the challenge text to the original one . If the challenge text matches then client is allowed to communicate and if challenge text is not matching the AP won’t allow client to join network
Wi-Fi Protected Access 2(WPA2):
Using PMK , PTK and GTK are derived from four way hand shake which is used to encrypt unicast and broadcast frame.
Lets consider the case of WPA2-PSK ,where after open security , we see 4-way handshakes as shown below
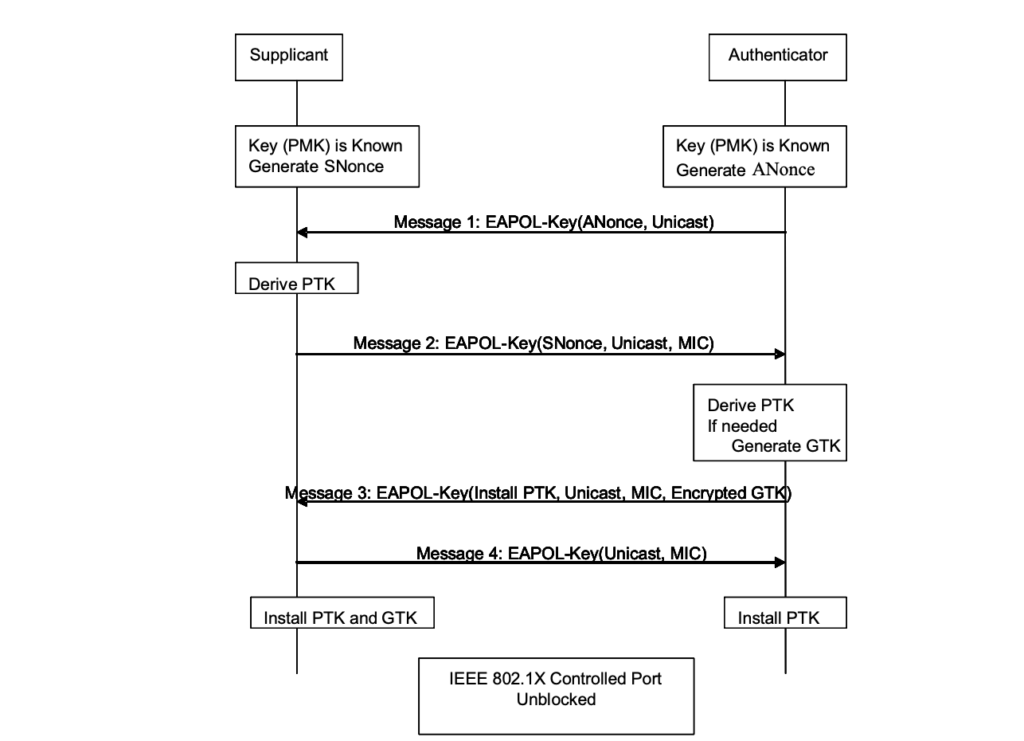
For case of WPA2-TKIP, GTK is not installed as a part of 4-way handshake hence two separate handshake takes place i.e

Sniffer capture for WPA2-PSK handshake:
Client connecting to AP using WPA2-CCMP mechanism
Note: Always look for Pairwise Cipher Suite and Auth key Management Suite

EAPOL1 ->Sent from AP to STA
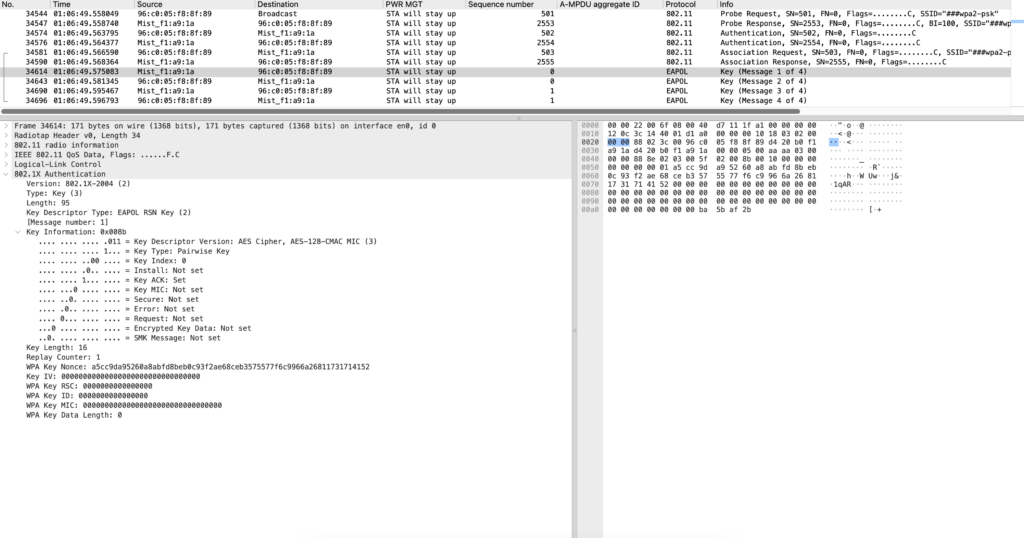
EAPOL2 ->Sent from STA to AP
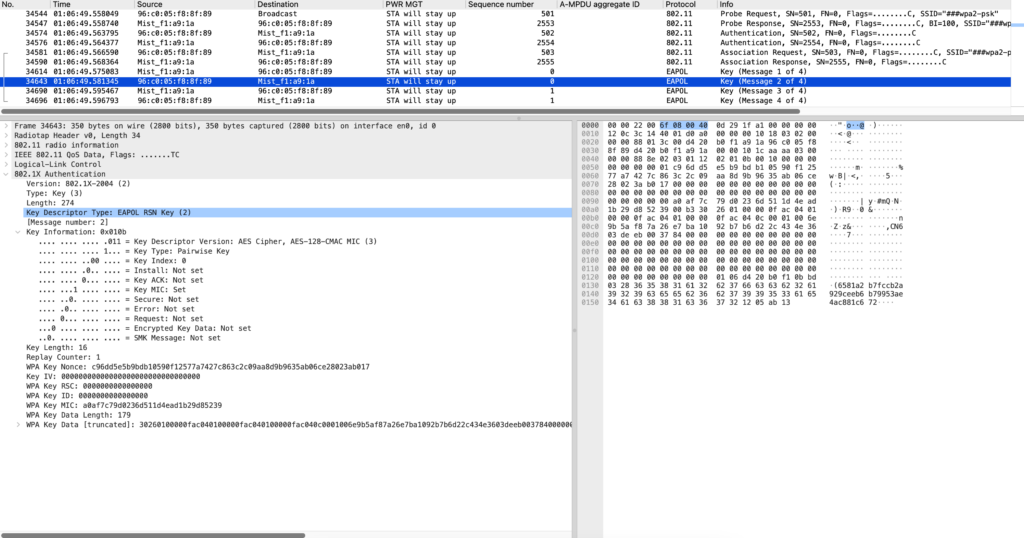
EAPOL3->Sent from AP to STA (install bit set)

EAPOL4 -> Sent from STA to AP (its more over a acknowledgement for EAPOL3)

References:
802.11-2007 Standard
CWSP Book
Note: All diagram or figure are taken from references