802.11 Frames are classified in three i.e data, management and control frame
Each of these frames has its unique purpose which can help to clients or stations to connect or join network and have reliable access to internet .
Data Frames are one that carries actual payload or data
Management frames are basically used by clients or station to join and exit BSS (basic service set)
Control frames are the one which are used to help deliver data and usually sent at basic rates
Basic frame format of 802.11 (Data Frame):
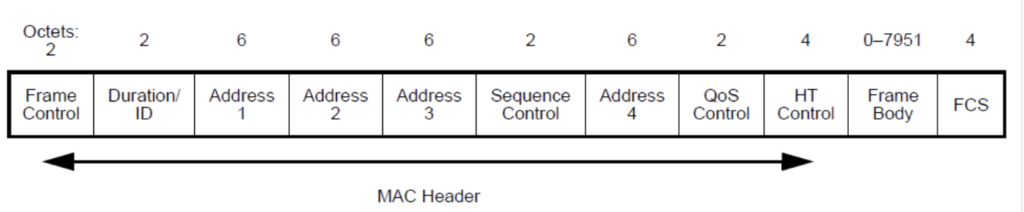
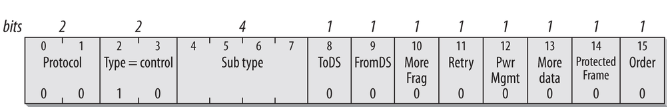
Frame control field:
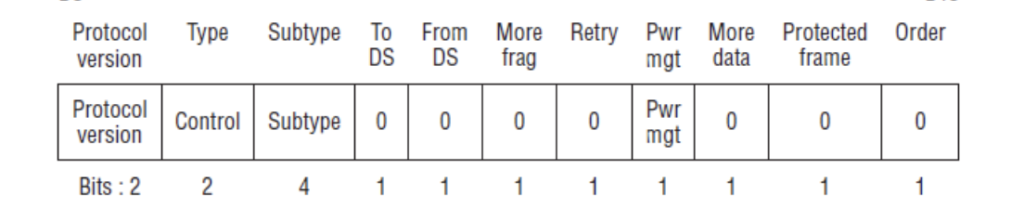
Protocol Version:
The Protocol version currently always set to 00 two bit, as this field may be used in future for new versions
Type and Subtype:
The Type subfield has two bits, whether it belongs to the data frame, control frame, or management frame category. This classification enables proper handling and processing of different frame types.
Type of management frames is 00, data frame is 10 and control frame is 01 and subtypes are as follows

Figure(i)
ToDS and FromDS and Address Field:
When To DS and From DS are both 0 then below will be the address added in 802.11 frame (Address 1 = Destination , Address 2 =Source ,Address 3 = BSSID)
When To DS field is 1 and From DS field is 0 then below will be the address added in 802.11 frame (Address 1 = BSSID,Address 2 = Source
,Address 3 = Destination)
When To DS field is 0 and From DS field is 1 then below will be the address added in 802.11 frame (Address 1 = Destination,Address 2 = BSSID,Address 3 = Source)
When To DS and From DS are both 1 then below will be the address added in 802.11 frame (Address 1 = Receiver,Address 2 = Transmitter
,Address 3 = Destination,Address 4 = Source)
More Fragments:
More Fragments subfield, observed in both data and management frames and this field inform regading additional fragments of the frame are yet to be transmitted.
Duration/ID:
The Duration/ID field is also called as Network Allocation Vector (NAV), Used to calculate time durations for transmitting frame.
Sequence Control:
The Sequence Control field ensures the proper arrangement of frames .
Frame Body:
It is actual data payload and length of the frame Body or payload may vary depending on device type or requirement.
Frame Check Sequence (FCS):
Used for error-checking purposes. It helps to identify potential corruption within the frame.
Qos Control Field:
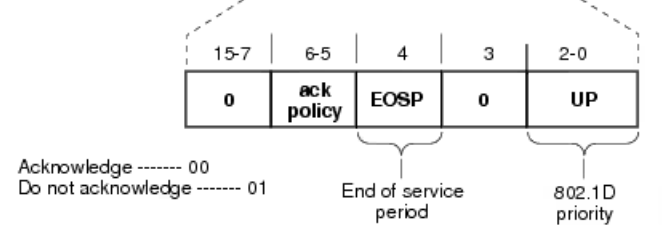
The QoS is used for improving the quality of service (QoS) in wireless networks. Implementation of QoS can help in prioritizing and managing network traffic.
The QoS control field adds a User Priority and this sub field indicates the priority of frame i.e higher priority receive highest preferences in terms of accessing the wireless medium.
HT Control:
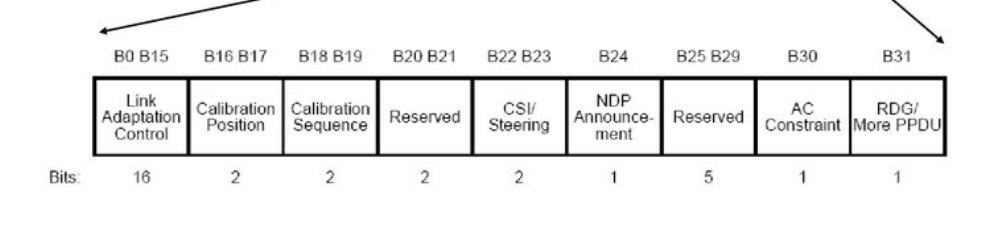
The High Throughput (HT) Control field used to optimize the high-throughput capabilities of WLAN network.
Link Adaptation Control: Provide information regarding modulation and coding scheme (MCS) to be utilized for communication.
Calibration Position and Calibration Sequence: Calibration generally used to optimize performance in WLAN network.
CSI Steering:While Channel State Information (CSI) pertains to the current state of the communication channel.
NDP Announcement : Used for sounding and measurements.
AC Constraint (Access Category Constraint):Sets Priority for differrent type of traffic, like voice, video, and best effort.
More PPDU (More Physical Layer Protocol Data Units):Used to refer data exchanged between devices at the physical layer.
Management Frames:
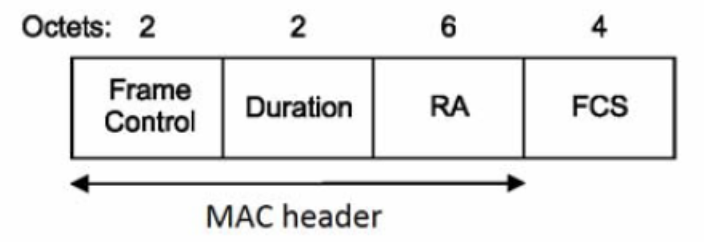
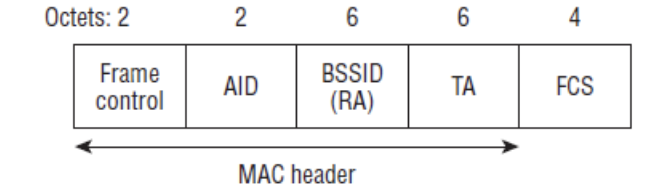
Management frame format always has below MAC address field i,e DA,SA,BSSID as shown in below Figure(ii)
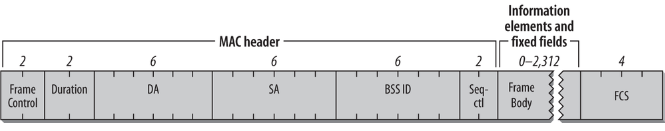
Figure (ii)
The first address field of management frame is used as DA i.e is Destination address.There are few management frames with a single BSS to limit the effect of broadcast and multicast management frames.
Duration calculation in management frames:
For contention-free period duration is always set to 32,768
When frames are getting transmitted in contention based then device or AP has to mgo through DCF or EDCA mecahnism for atomic exchange to complete.
a.If management frame is broadcast or multicast ,duration is set to 0 as broadcast and multicast frame don’t need to be acked
b.If management frame is part of multiframe exchange ,duration is set to milliseconds (management frame+3xSIFS+Ack)
c. if management frame is part of final fragment then duration is Ack+SIFS
Examples of Management frames:
Beacon Frame:
Beacon Frame is to provide essential information such as SSID, supported data rates, and security settings. It will be broadcast frame sent from access points,Station uses passive scan technology to scan for beacon and prepare scan list.
Probe Request/Response Frames :
Probe req sent from station to get detailed information about available network and Probe Response sent from access points to respond with the requested information.
Association Request/Response Frames:
Association Request frame sent by station while trying to join network. Assoc response from AP for confirming or denying the association.
Reassociation Request/Response Frames:
While station or client roaming between two access point station utilize Reassociation Request and Reassociation Response frames,
Authentication Frames:
Used by station’s to share capability with accesspoint before associating to it.
Deauthentication Frame/ Disassociation Frame:
When Access poin or station need to terminate its association it uses Deauth or Disassoc frame
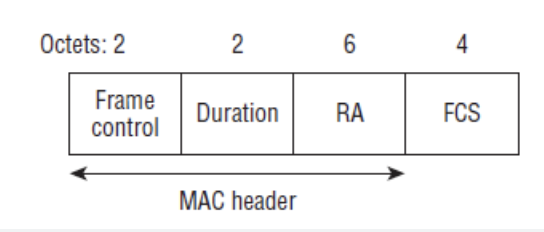
Control Frames:
Control frames helps data delivery between access point and clients.
Most of the control frames uses below frame control format :
Protocol version: Always it set to 0
Type : For control frames it set to 01
Subtype: For different control frame the subtype changes mentioned in figure(i) in
To DS/From DS: Always set to 0
More Fragment bit: Always set to 0
Retry bit: Control frame don’t have any retry mechanism so always set to 0
Power management bit: Used to indicate PM bit of sender
More data: Always set to 0
Protected frame: Control frames are not encrypted so its always set to 0
Order bit: it cannot be transmitted as out of order ,so always set to 0
ACKNOWLEDGMENT (ACK) FRAME :
Basic acknowledgment mechanism, the ACK frame aids in detecting and retransmitting frames that are not acknowledged.
REQUEST-TO-SEND (RTS) FRAME :
Help in reducing collision probabilities in a shared medium.

CLEAR-TO-SEND (CTS) FRAME:
As a part of the RTS/CTS mechanism,For every Request to send from station, access point respond with Clear to send.
BLOCK ACKNOWLEDGMENT (BA) FRAME:
Single acknowledgment for multiple frames, the BAR frame reduces overhead and improves network performance..
POWER SAVE POLL (PS-Poll) FRAME:
The PS-Poll frame allows devices to sleep and wake up periodically, helps in power consumption.
References:
1. learning.oreilly.com- Chapter 4
2.CWAP
Note: All diagram or figure are taken from references